In general, excavation means to loosen and take out materials leaving space above or below ground.
Sometimes in civil engineering term earthwork is used which include backfilling with new or original materials to voids, spreading and levelling over an area.
British Standard CP6031 gives standards and recommendation to earthworks covering embarkment and cuttings, levelling and compacting, and the use of earthmoving plants etc.
Excavation and earthmoving plants
Advantages of using mechanical plant in excavation :
a) work done quicker,
b) avoid dangerous condition of work by human workers, say, existence of ground water or collapse of soil,
c) achieve greater depth,
d) use fewer manpower and work done in lower cost (for larger scale work only)
Disadvantages:
a) involve larger running and maintenance costs,
b) require a larger operating area,
c) access provision to working area,
d) less flexible in work planning,
e) idling time increase cost of work,
Brief description of Earthmoving Excavation Plant & Machinery
1. Face shovel excavators:
This can be of cable or hydraulic operated, mounted on wheel or track.
They are fitted with µ±bucket which faces away from the machine.
Face shovel excavators are used for loosening, excavating vertical or near-vertical soil above the machine base level.
They are not suitable for horizontal or below ground excavation.
2. Back actors (Backhoe):
They are used for below ground level excavation.
The bucket acts downwards and drag towards the machine and tilted upwards to hold the loads.
Backhoe are used mainly as trench or large scale open excavation, but sometimes they are also used as loading machines.
3. Bulldozers:
They are traditionally track mounted tractor with significant weight so that they can work easier with soil.
Bulldozers are usually fitted with a straight or angled blade which can be slightly raised by hydraulic action to adjust level.
They are used for grading materials to levels over relatively smaller area, to cut small tree, remove surface vegetation or hard surfaces etc.
The max cut is about 400 mm below base of the machine.
4. Tractor shovel (loading shovel ):
This machine is similar to a bulldozer but has a hydraulic operated bucket in place of the blade.
Materials above the base of vehicle can be lifted and unload onto a dump truck or onto a spoil heap.
The bucket size varies from 0.5 cubic meter to 3 or 4 cubic meter depending on capacity of machine.
5. Clamshell excavator:
This is somewhat a crane, usually track mounted, and hanging a wire operated clamshell at the jig.
It is used to handle or load soft /saturated soil on site.
Clamshell excavator is more useful in very big site where a large amount of soil materials is required to be removed.
6. Powered shovel or drill:
This is for cutting of larger boulders or rock.
Usually the drill is pneumatically operated and mounted on a tracked base.
Very often, it is convertible to a backactor with the bucket replaced by the drill to gain flexibility and minimize capital input.
7. Grader:
It can be a self-contained power unit or a towed vehicle by a tractor.
A grader does not excavate but it levels and grades out to fine loose or deposit materials.
A centrally mounted blade much narrower and flatter than a bulldozer’s serves the purpose.
It skims the surface of soil evening out the bumps and hollows.
The blade can be lowered or lightly tilted to adjust for the level of the graded surface.
8. Scraper:
The machine works similarly to a grader but it has a container to hold the surplus soil after scraper.
The container which is filled with soil can also serve the purpose of backfill of hollow ground.
9. Dumper:
This is a smaller vehicle with a tipping hopper or skip designed to carry material within a site.
The hopper is usually front mounted to provide better control by the driver.
It is easy to maneuver on uneven and rutted ground.
Capacity of the hopper varies from 1 to 3 cubic meter depending on the size of dumper.
10. Dumper truck:
Designed for large-capacity loads to be carried over a long distances on or off site.
Normal capacity ranging from 5 to 15 cubic meter, some even up to 50 meter cube or above.

Government Regulation in controlling excavation
Excavation work to certain extent is dangerous so governments have imposed regulations to control over works where large scale excavation is involved.
Some of these regulations are in:
1. Building (Administration) Regulations
2. Building (Construction) Regulation
3. Relevant Practice Note for Authorized persons and Registered Engineers etc.
These requirements apply to excavation:
1. Deeper than 4.5m and exceed 5m in length (4.5m up from base)
2. Liable to affect any road, building, slope steeper than 30o or water main bigger than 75mm in diameter
3. Supporting proposal to be submitted and obtain consent before starting of excavation.
Content of excavation proposal should include the following information:
1. Detail of method for ground protection treatment and dewatering.
2. Survey of existing site condition
2.1 accurate level survey
2.2 geotechnical survey
2.3 ground and surface water information
2.4 record/report of the surrounding facilities and structures
3. Detail design or construction proposal regarding:
3.1 site/soil investigation report and geotechnical assumptions
3.2 detail of excavation/protection works
3.3 sequence and method of works
3.4 monitoring proposal
3.5 other information or specification that deem necessary
EXCAVATION WORKS
Excavation in most situations nowadays is done by mechanical means. Very large scale excavation requires tremendous resources input and careful work planning both for building and civil engineering works.
However, the exact method to be adopted still depends upon a number of factors:
1. Nature of subsoil – affect type of machine used and the necessity of soil protection.
2. Size of excavation – affect type of machine used and method to excavate.
3. Scale of work – large volume of excavation may involve complicated phasing arrangement and work planning
4. Ground water condition – affect degree of protection (watertight sheet piling or dewatering may required.)
5. Surrounding condition – impose certain restrictions and precautions (eg. diversion of a government drain, or underpinning work to the nearby building foundation)
Deep excavation
Deep excavation, unlike a shallow one, often requires to protect the sides of cut using suitable support.
Besides, the problem of ground water cannot be avoided, there are methods to overcome this, such as:
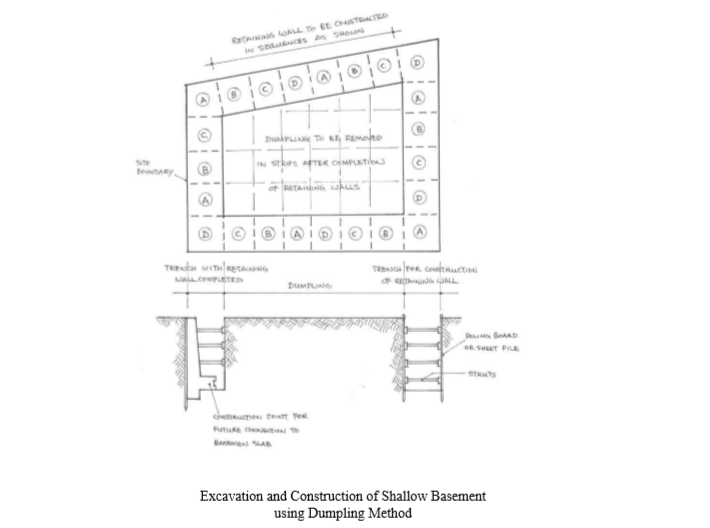
1. Dumpling method
This is used where there are buildings or street in the proximity.
The method is to construct a series of retaining walls in trench, section by section, around the site perimeter, leaving a centre Called “dumpling”.
When the perimeter walls are in place, excavation may start at the centre of the dumpling, until exposing a section of the wall.
Then the wall may be side supported by struts, shoring or soil anchor etc., again section by section in short length, until the excavation is all completed.
This method does not require much heavy mechanical equipment and thus cost of work is relatively lower.
It can excavate up to a maximum depth of about 3 meter.
Sometimes in very poor soil or in waterlogged ground, interlocking steel sheet pile may be driven to confine the area to be excavated.
After that excavation can be done in sections and properly supported similar to that mentioned above.
By using the sheet pile, excavation may reach maximum to about 15 meter, however, in this case the cost of work will increase.
2. Diaphragm walling Method
This method is adopted where it is necessary to construct a R.C. retaining wall along the area of work.
Because the wall is designed to reach very great depth, mechanical excavating method is employed.
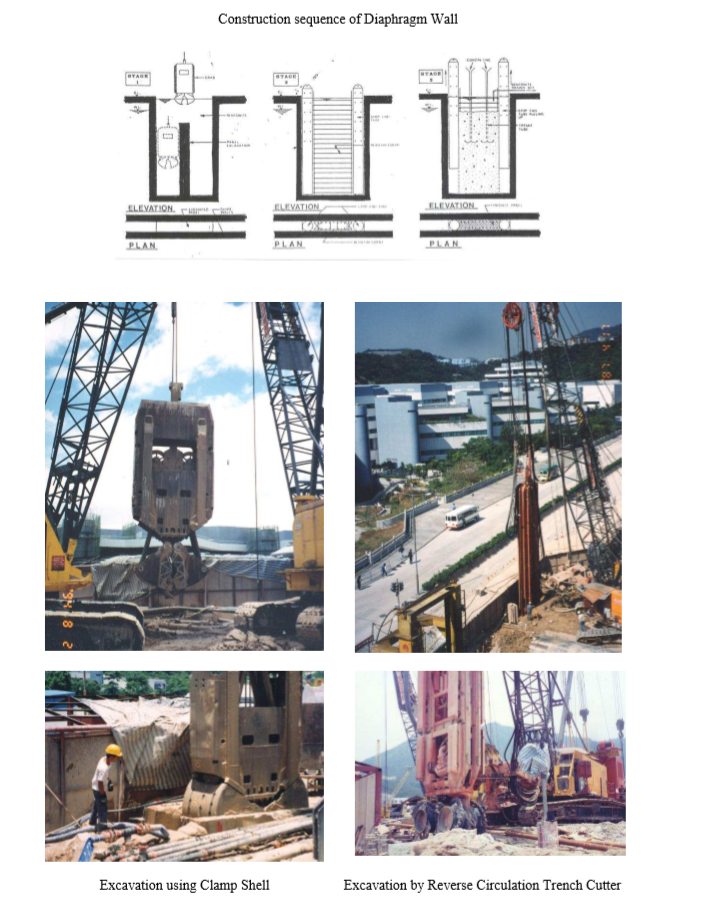
Typical sequence of work for diaphragm walling includes:
a) Construct a guide wall
b) Excavation for the diaphragm wall
c) Excavation support using bentonite slurry
d) Inert reinforcement and concreting
Construct a guide wall: guide wall is two parallel concrete beams running as a guide to the clamshell which is used for the excavation of the diaphragm wall.
Excavation for the diaphragm wall: In normal soil conditions excavation is done using a clamshell or grab suspended by cables to a crane. The grab can easily chisel boulder in soil due to its weight.
Excavation support: excavation for the diaphragm wall produces a vertical strip in soil which can collapse easily. Bentonite slurry is used to protect the sides of soil. Bentonite is a naturally occurring clay which, when added to water, forms an impervious cake-like slurry with very large viscosity. The slurry will produce a great lateral pressure sufficient enough to retain the vertical soil.
Reinforcement: reinforcement is inserted in form of a steel cage, but may require to lap and extend to the required length.
Concreting: concreting is done using tremie. As Concrete being poured down, bentonite will be displaced due to its density is lower than concrete. Bentonite is then collected and reused. Usually compaction for concrete is not required for the weight of the bentonite will drive most of the air voids in concrete.
Joining design for the diaphragm wall:
Diaphragm walling cannot be constructed continually for a very long section due to tremendous soil pressure.
The wall is usually constructed in alternative section.
Two stop end tubes will be placed at the ends of the excavated trench before concreting.
The tubes are withdrawn at the same time of concreting so that a semi-circular end section is formed.
Wall sections of this type are built alternatively leaving an intermediate section in between.
The interior sections are built similarly but without the end tube.
At the end a continual diaphragm wall is constructed with the sections tightly joined by the semi-circular groove.
3. Using Cofferdams in Excavations
A cofferdam can be defines as a temporary box structure constructed in earth or water to exclude soil or water from a construction area such as for basement or foundation works.
Use of cofferdam suitable for excavation of larger scale can be of:
a) Sheet pile cofferdam:
Also known as single skin cofferdam.
Interlocking type steel sheet pile is used and can be used for excavation up to 15 meter.
Sheet pile in this case acts as a cantilever member to support the soil therefore adequate depth of pile or suitable toe treatment may be required.
In addition, cofferdams are needed to be braced and strutted or anchored using tie rods or ground anchors.
b) Double skin cofferdam:
This works similarly like the sheet pile to form a diaphragm.
However, the diaphragm is double-skinned using two parallel rows of sheet pile with a filling material placed in the void between.
This creates somewhat a gravity retaining structure and increases the ability to counteract the soil behind.
For this method more working space is required.
Sheet Steel Piling
Steel, amongst other materials such as timber, is most effective to be used as sheet pile due to its high tensile as well as their interlocking ability.
It can be used as timbering to excavation in soft and/or waterlogged soils especially in congested site where there is no enough space for complicated shoring.
Steel sheet pile can be of numerous shapes, thickness and sizes.
Most of them can be water tight and for some heavy sections they can be driven down to 15 meter depth.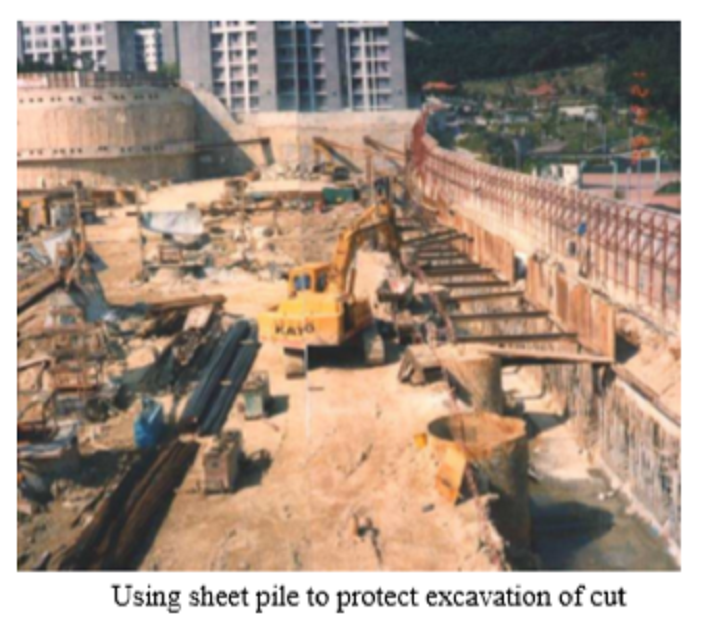
To erect and install a series of sheet piles and keep them vertical in all directions a guide frame may be required.
The piles are lifted by a crane, using the lifting holes near the top of each pile, and positioning them between the guide walling of the guide.
Powered hammer (fitted with a grip to the pile) which are hanged by the crane is usually used to drive the pile.
Sometimes hydraulic hammer can be used to reduce noise.
There is a tendency of the piles to lean to a direction during driving, therefore , special control is required to monitor that the pile is vertical all the way through.
Ground anchor
Ground anchor is basically a pre-stressing tendon embedded and anchored into soil or rock to provide resistance to structural movements by a “tying back” principle.
Common applications of ground anchor are:
1. General slope stabilization
2. Tying back/stabilizing a retaining structure
3. Tying back/stabilizing for diaphragm walls, but for a temporary nature during excavation
4. Tying back the entire building from up possible uplifting
Ground anchor can be classified into:
1. Rock anchor – for anchorage in rock
2. Injection anchor – suitable for most cohesive and non-cohesive soils
Method to form a ground anchor
A hole is predrilled on soil or rock in position carefully calculated.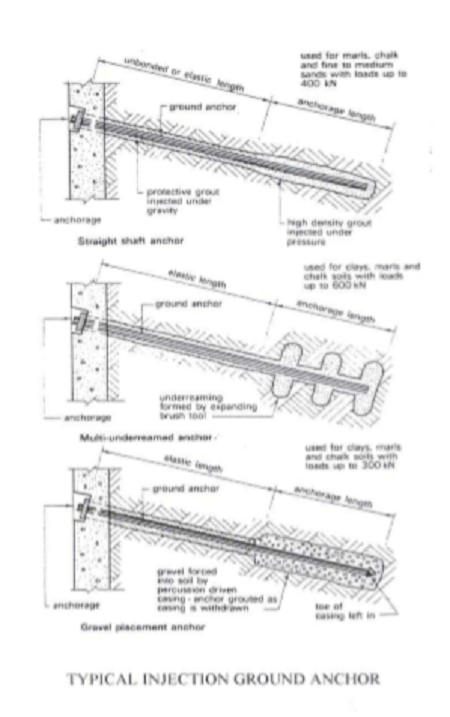
For rock anchor, an anchor bar with expanded sleeves at the end is inserted into the hole.
A dense high strength grout is injected over a required length to develop sufficient resistance to hold the bar when it is stressed.
Stressing is by hydraulic mean and when the stress is developed, the head of the bar is hold by an end plate and nut.
For injection anchor, a hole should be bored usually with an expanded end to increase anchorage ability.
The pre-stressing bar is placed into the bore hole and pressure grouted over the anchorage length.
Gravel placement ground anchor can also be used in clay soils for lighter loading.
In this method irregular gravel is injected into the borehole over the anchorage length to form an end plug.
The gravel plug is then forced into soil using percussion method through casing, forming an enlarged end.
A stressing bar is inserted into the casing and pressure grouted over the anchorage length as the casing is removed.
It should be noted that certain protection measure against corrosion or rusting is required for the stressing bar.
Usually, the bar may be coated with bitumen, wrapped by greased tape or filled with non-pressurized grout after stressing is completed.

Ground Water Control / Dewatering Techniques
Groundwater is the water which is held in the soil, either in a non saturated, saturated or over saturated form.
Water table is a line showing the change of water content in soil, below which soil is saturated with water.
Water in soil often acts as a lubricant, which increases the tendency of soil to slip or slide.
Besides, it causes certain difficulties and danger in case of excavations to be done.
In some soils, such as non-cohesive soil with coarser grain composition, water can flow through the grain particles.
While for cohesive soils, water cannot flow due to the large capillary held by the very fine soil particles.
Keeping out the ground water
Ground water can be kept out either permanently such as for long term waterproofing for a basement, or temporarily such as to ease work during excavation.
The following provisions can contribute certain degree of water-tightness to the basement during the construction:
1. Sheet piling
2. Diaphragm walls
3. Suitable grouting to the sub-soil
In addition, ground water can be further controlled by the use of the following arrangements:
1. Sump pumping
2. Well point dewatering systems
3. Shallow or deep-bored wells
4. Horizontal ground water control
5. electro-osmosis method
Grouting
Grouting is often used to stop the penetration of water in sub-soil with high permeability, such as in fissured and jointed rock strata.
Rows of holes are bored on the soil and, usually cement grout, are injected under high pressure.
The cement grout will penetrate into the voids of the sub-soil and form somewhat an impermeable curtain vertically separating the ground water.
Cement grout is usually a mixture of cement and water, or cement and sand under ratio maximum 1:4.
Sometimes chemical grout can be used to form a gel which can increase strength and reduce permeability of soil (eg. Sodium silicate + calcium chloride = calcium silicate, which is a silica gel)

CONSTRUCITON OF BASEMENT USING TRADITIONAL METHODS
Construction of basement is difficult because it must be carried out below deep ground in adverse conditions such as existence of ground water, muddiness or limited working space.
Besides, works are needed to be done amidst layers of props, struts, walling and shores, which cannot be removed until the permanent works are completed and capable of carrying the final loads.
For each case of basement construction, the method of soil support, sub-soil condition, structure of the basement as well as the layout requirement of the entire building must be taken into consideration before designing the method of basement works.
Method of constructing ordinary basement
One of the most effective methods to construct ordinary basement is by the use of diaphragm wall or sheet pile wall (cut-off) which serves as a retaining structure during excavation and as the sides of the basement walls.
When the central soil is removed during excavation, the cutoff wall should be properly supported for works.
Below are some suggested methods:
1. Use of lattice beams: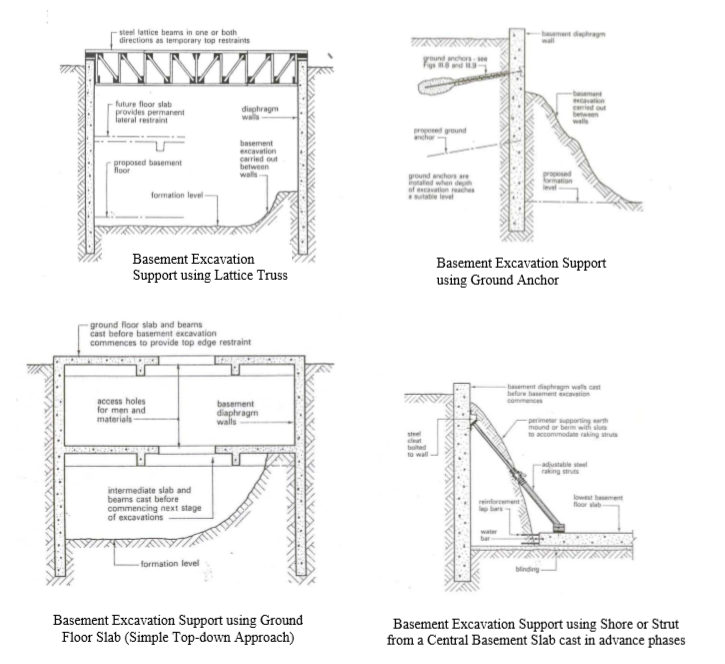
A series of lattice beams or steel trusses are installed so that they span between the top of opposite diaphragm walls enabling them to act as propped cantilevers.
The trusses can be removed after the internal floors have been constructed and receiving all the lateral forces from soil.
2. Use of Ground Anchors:
Diaphragm walls are exposed by carrying out the excavation in stages and ground anchors are provided to stabilize the walls as the works proceeds.
This method is most effective for basement of very large span or without intermediate floors as lateral support
3. Construct floor slab as support (top-down method):
After the perimeter diaphragm walls have been constructed, the ground floor slab and beams are cast providing tip edge lateral support to the walls.
An opening is left in the slab for labors, material or plant as access to continue excavation to the lower stages.
This is repeated until the required depth is reached.
4. cast the centre basement slab to support struts:
Centre area between the diaphragm walls can be excavated leaving an earth berm around the perimeter to support the walls whilst the lowest basement floor in centre can be constructed.
Slots to accommodate raking struts acting between the wall face and the floor slab are cut into the berm.
Final excavation and construction of the remaining of the basement can take place in stages around the raking struts.

5. Construct the basement using in-situ reinforced concrete and tradition formwork system
The basement structure can be constructed upon the completion of the excavation with the basement pit properly formed and supported.
Usually this is done in a bottom-up arrangement using in-situ reinforced concrete formed by traditional timber formwork.
However, all the works are to be done in the congested underground environment inside the basement pit with a lot of lateral supporting frame and work in confined space.
Special attention including accurate construction planning and special design to allow room for the erection of the formwork as well as for the placing in of the required materials and equipment’s, safe access etc. should be provided.

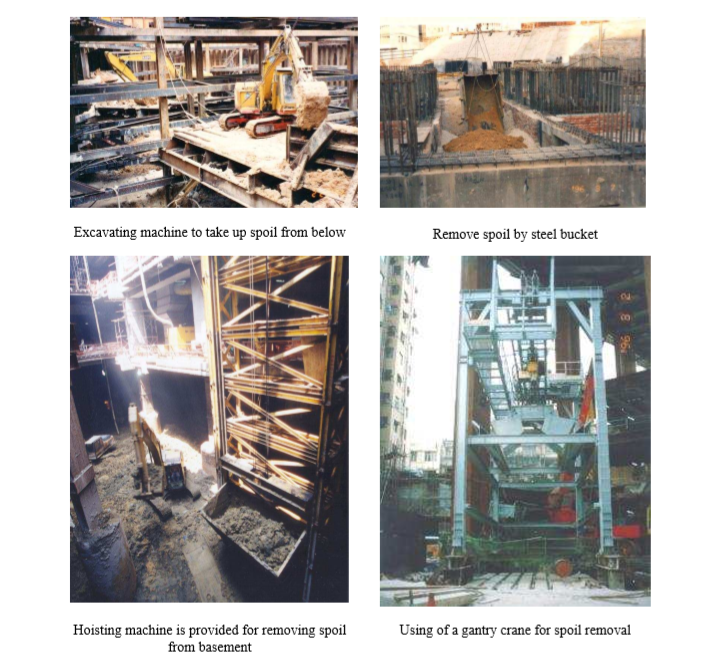
Removal of Soil
There is always great amount of excavated soil is produced during the process of excavation.
Suitable planning for the removal of the excavated material should be made in advance in order not to cause disruption to work and incur extra costs.
Soil removal can be done by the following ways:
a) Using manual method, say, by wheel barrow.
b) Using bucket and lift to ground level by crane.
c) Using hoist rack (opening has to be provided in the basement/excavation pit first).
d) Using gantry crane (opening has to be provided in the basement/excavation pit first).
e) Using conveyor belt
f) Using excavating machine to removal spoil, may be in stepped position in case of very deep pit.
g) Using dump truck but access provision has to be provided in advance (such as a temporary ramp or the permanent vehicular access into a basement)
Waterproofing the basement
Water tight basement wall is an essential element to waterproof a basement, however, due to the basement walls are often constructed under complicated phases to match with the excavation sequences and this may increase the possibility of leaking, therefore, careful construction joining design is essential to ensure the basement structure is perfectly waterproofed.
Very often providing the water stops into these joints is helpful.
However, the most widely used method to water-proof a basement is to provide a cavity to the wall of the basement (by building a skin wall to the sides).
The ground water leaks into the basement can then be collected through concealed channel to a sump pit and removed by pumps.
References:
1. Civil Engineering Construction – by J.M. Antill, Paul Ryan and G.R. Easton (McGraw Hill 1988)
2. Civil Engineering Technology – by B.G. Fletcher and S.A. Lavan; (Butterworths 1982);
3. Civil Engineering Construction – by B.G. Fletcher and S.A. Lavan (Heinemann: London 1987)
4. Introduction to Civil Engineering Construction – by Roy Holmes (College of Estate Management, 1996)
Discover more from Method Statement Store
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.