Below we have listed 19 toolbox talk topics with briefing which should take place during the daily safety meeting.
Below is table of content which is covered in this post about the safety meeting topics.
- Sun Safety
- Work at height
- Mobile scaffolds
- Portable electric equipment
- Coshh
- PPE-Head
- PPE-Hand
- PPE-Foot
- PPE-Hearing
- PPE-Eye
- Accident reporting
- Fire Precautions
- Flammable liquids
- Manual Handling
- Ladders
- Safety Signs
- Housekeeping
- Reversing vehicles
- Cartridge Hammers etc.
For every day records and for each activity proper documents shall be maintained refer below sheet for reference:
| Name of Person Giving the Talk | ||
| Topic of the TBT / Safety Talk | ||
| Date: | ||
| Start Time: | ||
| Finish Time: | ||
| Duration: | ||
| Attendees Name | Signature of Attendee | Comments |
Now lets see each activity one by one.
Toolbox Talk Sun Safety
Company is committed to protecting and educating its workers about the risks to health arising from excessive exposure to strong sunlight.
The policy will be implemented as appropriate for all workers who are at risk.
Sun protection advice will be provided as part of routine health and safety training for all employees, including supervisors and managers.
All new employees will be made aware of the Sun Safety Policy.
Wherever possible, working hours and tasks will be scheduled to avoid the midday sunshine.
Wherever possible, work that can be carried out indoors or in the shade will be scheduled during periods of strong sunshine.
i. All workers who are liable to be at risk will receive appropriate training on how to protect themselves from prolonged exposure to strong sunlight, regardless of their skin type or hair color.
ii. Workers who are at risk will be encouraged to wear full-length trousers and long-sleeved shirts throughout the year. They will be made aware that, ideally, clothing will be loose fitting and made from a close-weave fabric.
iii. In most circumstances, the mandatory wearing of a safety helmet will provide the necessary protection for the head. In the rare circumstances where a safety helmet need not be worn, workers at risk will be required to wear a hat.
iv. Workers at risk will be given information on the appropriate use of sunscreen creams, including advice on the minimum recommended level of protection.
v. Drinking water will be provided via the wash area in the shade and all workers at risk will be encouraged to drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
vi. Rest areas in the shade will be provided and workers at risk will be encouraged to use them for their rest breaks.
Toolbox Talk Work at height
Falls from height accounted for maximum fatal accidents at work and major injuries all the times. They remain the single biggest cause of workplace deaths and one of the main causes of major injury.
New Regulations regarding work at height have been introduced and they apply to all work at height where there is a risk of a fall liable to cause injury.
Regulations place duties on employers, the self-employed, and any person.
As an employee you must:
i. report any safety hazard to your supervisor
ii. Use the equipment supplied (including safety devices) properly, following any training and instructions (unless you think that would be unsafe, in which case you should seek further instructions before continuing).
As employers we must ensure:
i. All work at height is properly planned and organized;
ii. All work at height takes account of weather conditions that could endanger health and safety;
iii. Those involved in work at height are trained and competent;
iv. The place where work at height is done is safe;
v. Equipment for work at height is appropriately inspected;
vi. The risks from fragile surfaces are properly controlled; and
vii. The risks from falling objects are properly controlled.
It is also required that any platform used for (or for access to) construction work and from which a person could fall more than 2 meter is inspected in place before use and every seven days there after.
Companies have been criticized for removing edge protection and not replacing it immediately, if it is required to remove guard railing/toe boards for the purpose of loading out while the railings/boards are removed persons must vacate the area, post a sentry to stop others wandering in the area, load out and then replace any removed protection immediately.
Sub contractors are advised that if they go to a work in an area where other trades have removed guard railing, they must report to site supervisor immediately for further instructions.
Remember we all want to go home safely and uninjured
Toolbox Talks-Mobile Scaffolding
Scaffold towers must be constructed to the same standard as any other scaffolding.
i. Tower must be inspected before first use.
ii. Competent persons must only erect scaff towers.
iii. Working platforms must be fully boarded out and where there is a risk of fall from height they must be fitted with guardrails and toe boards.
iv. Brakes must be applied before tower is used. Wheels must be checked to ensure they are firmly fixed.
v. Mobile scaffolds used outdoors must be such that the height of the platform is no more than 3 times the smaller base dimension.
vi. Mobile scaffolds used indoors must be such that the height of the platform is no more than 3.5 times the smaller base dimension.
vii. The access ladder must be securely fixed.
viii. A mobile scaffolding must never be moved when persons or material are still on the tower.
ix. Towers should be erected and dismantled carefully along with manufacturers instructions to avoid damage to components / parts.
x. If scaff tower appears to be unsafe, do not use it report it to your supervisor.
xi. Never use ladders/steps/milk crates to gain extra height.
Toolbox talks Scaffolding
Lots of different scaffolds are in use today but all have the same basic safety rules:
i. Ensure handover certificate has been received/and or that a competent person has inspected the scaffold as safe in the last 7 days or following extreme weather conditions.
ii. Check the scaffold is fully boarded out.
iii. Check the guardrails and toe boards are fitted suitably.
iv. Check the ladder access is secure by using the ties.
v. Check the scaffold is on a sound base and sole plates have been used.
vi. Never use a scaffold that you think is unsafe check with your supervisor in case of any doubt.
vii. Do not overload platforms with materials and keep platforms free from debris.
viii. Competent persons must only carry out alterations if needed.
ix. At the end of the day remove the ladder or board to prevent children playing on them.
Toolbox talk TBT Portable Electric Tools
Before using an electrical tool makes sure that:
i. Portable appliance test date is in date. If not contact a competent electrician.
ii. That the casing is undamaged, if damaged take away and don’t use.
iii. Use tools only of the correct voltage safest voltage is 110 volts.
iv. Make sure the cable is long enough to reach your work area without straining it but be aware of trip hazards.
v. Keep cables off the floor where possible especially on stairways and access routes.
vi. Only use the tools for designated purpose.
vii. Never connect a portable appliance to a lighting socket.
viii. Never use worn out or damaged appliances.
ix. Disconnect tools when not in use.
x. Electricity kills take faulty equipment out of use immediately.
Tool box Talks – COSHH
Many hazardous substances are used daily in the construction project work.
Accidents can be prevented if operatives understand what are the hazard areas and what precautions should be taken while using the hazardous substances:
i. Your supervisor will have a COSHH assessment for all chemicals that you need to use look at it and question if you do not understand it.
ii. Always read the label. Do not assume because containers look the same that they contain the same chemical. Check for danger symbols.
iii. Never put chemicals in another container which is not for that substance.
iv. When opening containers hold a rag over the cap as some times some liquids will spurt up on opening.
v. Always check what person protection PPE you need before handling chemicals.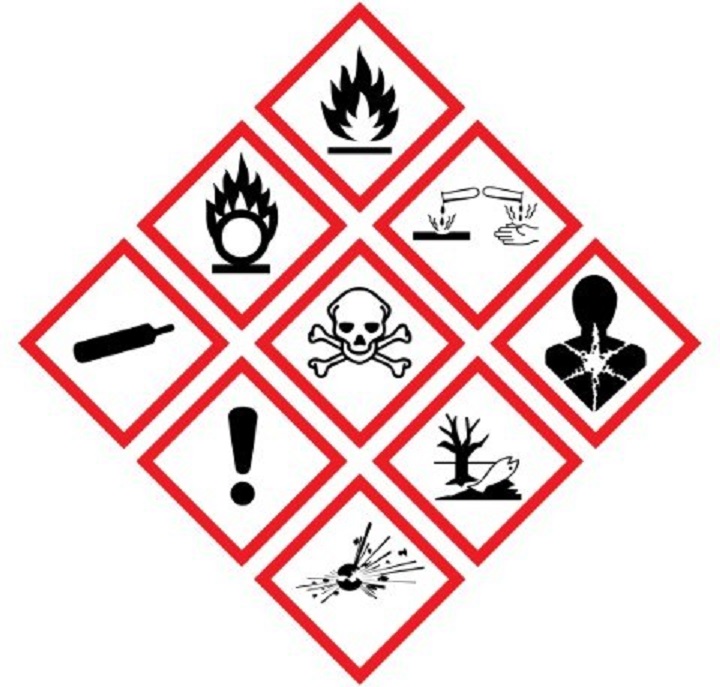
vi. Check the date on chemicals before use as they can become unstable if expired.
vii. Never smoke or undertake hot work in vicinity to flammable liquids.
viii. Never eat drink or smoke when handling chemicals remember to wash your hands.
ix. Good ventilation is important when using many chemicals check the COSHH data, if you feel unwell report to your supervisor immediately.
x. Use the smallest quantity of chemical necessary to do the job.
xi. If you are injured or affected by a chemical immediately report to get the first aid taking in account the MSDS chemical or Coshh data sheet etc.
xii. Report spillages and clear up as required by following the COSHH data sheet.
Head Protection Toolbox Talks
Accidents to the head are fatal protect your head. The construction Head protection Regulations were introduced to reduce injuries, all workers on construction sites must wear hard hats, where there is a risk of head injury
i. Always fit the headband to allow a perfect fir to your head.
ii. Check the shell for cracks, dents and other visual damage.
iii. Never paint the shell as this may weaken the structure.
iv. Use a chinstrap where there is a possibility that the helmet may fall off.
v. Do not punch holes in the hat for ventilation.
vi. Replace the helmet if it suffers a heavy impact.
vii. Keep your hat in good condition and replace after every 2 years.
Toolbox talk –PPE (Hand & Foot Protection)
Hands and fingers are always getting injured as they are very vulnerable to cut, crush and COSHH type injuries.
i. Ensure where guards are provided they are used, examples are cutting wheels, saws etc. and use push sticks where applicable.
ii. Crush injuries occur when using tools such as hammers incorrectly. If tools are defective replace or repair. Make sure in running nip points on machines are guarded properly.
iii. Skin allergies such as dermatitis can become long-term problems, avoid skin contact by wearing gloves and barrier cream. Always wash and dry hands and report rashes to your supervisor.
iv. Wear the right type of gloves for the right job.
Two main types of foot injuries are treading on sharp objects such as nails, which pierce the foot, and objects dropping on the foot.
The risk of foot injury can be reduced by the use of correct footwear.
Your employer must provide suitable footwear and you must look after it, use it and report any defects.
Hearing Protection Toolbox Talks
Noise damages your hearing. Noise induced hearing loss is irreversible. It can cause ringing or rushing noise in the ear.
If you feel that you are getting used to noise you have properly lost some of your hearing forever.
i. If you need to shout to be heard at about 2 meters it is likely there is a noise problem.
ii. Wherever possible noise should be reduced to an acceptable level where this is not possible ear protection must be worn.
iii. Earplugs/muffs must be fitted as per manufacturers guidelines, ask if you are not sure.
iv. Never insert plugs with dirty hands.
v. Regularly inspect ear muffs /plugs for any kind of damage.
vi. Wear hearing protection where there are warning signs.
Toolbox Talks –PPE (Eye Protection)
Eye protection must be worn when there is a risk of injury to the eyes.
Examples of activities include:
i. Cutting bricks or blocks with anything other than a trowel.
ii. The use of cartridge fixing tools.
iii. Dusty atmospheres.
iv. Striking of masonry nails.
v. Use of compressed air to blow down.
vi. Drilling cutting or breaking metal or concrete.
vii. Welding or cutting steelwork.
viii. Handling brushing or spraying chemicals where splashing is likely.
Wear the right glasses/goggles that are correctly fitted for the job in hand.
Look after your eye protection PPE, report any faults and replace.
Accidents and First Aid – Toolbox Talk
If you have met with an accident you must get first aid help and report the accident in the accident book.
It is for your own protection.
The accident must be reported as soon as possible.
If someone else has an accident call for first aid assistance immediately.
In the case of an accident site is left undisturbed to ensure that proper investigation can take place.
Minor accidents can lead to death.
Little injuries can lead to blood poisoning, which can be fatal.
Always know where your first aiders and boxes are located.
Never take equipment from a first aid box to self-treat get help from a first aider only.
Toolbox Talks –Fire Precautions
Good housekeeping and fire prevention go hand in hand.
Fires can start from:
i. Accumulated debris.
ii. Misuse of compressed gases or flammable liquids.
iii. The ignition of waste materials such as wood shavings.
iv. Not keeping heat away from flammable materials.
v. Always check your extinguishers for accessibility and make sure these are in good condition.
vi. Do not be careless when drying clothe etc.
vii. Do not allow rubbish to accumulate in the working areas.
Necessary Information
i. Know where to go if there is a fire.
ii. Always know where the extinguishers are and if it is found expired or empties report it immediately.
iii. Know which type of extinguisher is effective for fighting different type of the fires:
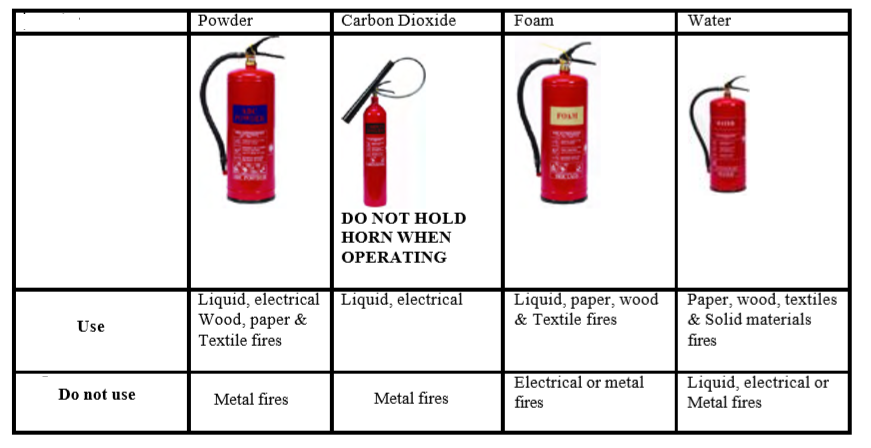
Toolbox Talk Abrasive wheels Topic
i. No one should change the abrasive wheel on any type of grinding machine unless he has the required training and has been appointed in writing by his employer to do so.
ii. Machine on which wheel to be mounted must have a maximum permissible speed in r.p.m.
iii. Wheels must not be operated at speeds in excess of the marked r.p.m.
iv. When the wheel is in motion the guard must be in position and must enclose the wheel except the part that must be exposed for the purpose of the cutting/grinding work.
v. When using or in the vicinity of a working abrasive wheels goggles must be worn.
vi. If dust is created when using a grinder or cutter, wear a suitable dust mask.
vii. Users and those in immediate vicinity also require to wear the suitable hearing protection.
Toolbox Talks Topic Flammable liquids
Many of the materials, liquids and substances which we use on sites are highly flammable e.g. solvents, petrol, cellulose based paints and thinners etc.
These types of materials must be kept in secure containers.
Containers used for petrol should be clearly marked “ Petroleum Spirit-Highly Flammable”.
Any empty container should be marked empty and stored away from the full containers.
Small containers carrying highly flammable liquids should be stored in fire resistant cabinets and bins.
Gas cylinders on site:
i. Must be stored in open air out of direct sunlight and away from ignition sources.
ii. The cylinders must be stored in an upright position and chained.
iii. Signs marked “Highly flammable-LPG” should be displayed in and outside the storage area.
iv. Any empty cylinders shall be marked empty and stored apart from full cylinders.
v. Sufficient number of powder extinguishers should be available around the storage compound.
vi. Smoking must not be allowed around and inside gas storage areas.
Toolbox Talks Topic of Manual Handling
Manual handling causes almost a quarter of all injuries at work.
Most of the injuries are to the hands, feet and back.
Some of the back injuries result in permanent disability.
When considering what you are moving consider the environment, the load, the individual.
Wherever possible avoid manual handling by using other means such as:
i. Mechanical handling – If you are trained.
ii. Wearing the right protective equipment.
iii. Know your own capabilities.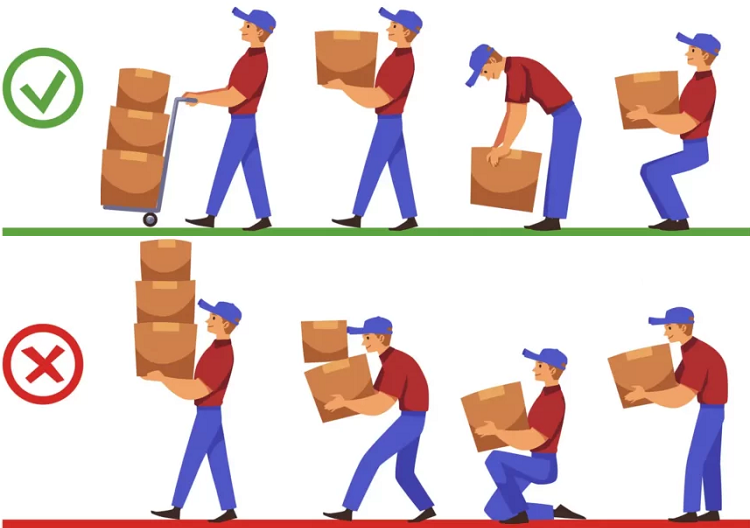
iv. Plan your lift.
Think thoroughly About the job i.e.
i. Can you handle the load by yourself or do you need help.
ii. What is the suitable route
iii. Will packing be required when stacked.
iv. What is the weight of the load.
v. Is the load stable.
vi. Any sharp edges etc.
Know the correct method of lifting
Stand close to the load with firm footing with feet facing forwards about 300mm apart.
Bend your knees to get down to the load not your back.
Place hands where they will not slip and grip firmly.
Straighten up with the legs keeping the spine as straight as possible.
Hold the load close to the body.
Ensure the load does not restrict your view.
Lift slowly and smoothly avoid jerking.
Put down in reverse order of lifting.
If team handling, nominate person to give instructions and where possible people should be same height and capability.
Toolbox Talks About Ladders
Work can only be carried out from a ladder when the job is of short duration and can be safely with three-point contact.
Remember:
i. Never overreach at the working position.
ii. Before using a ladder inspect it to see it is not damaged.
iii. Check the rungs and styles for splits and cracks.
iv. See that none of the rungs are missing or loose or having painting (Painting can hide faults).
v. Never repair a ladder take it away from use.
vi. Ladders should be on a firm base at an angle of not too steep and not too flat. Remember 1 up for 4 out.
vii. If the ladder can not be tied a second person must foot the ladder.
viii. When the work on ladder is finished, put it away to stop children playing with it.
ix. Make sure your footwear is clean before using a ladder i.e. oily shoes can cause slip from ladder.
Toolbox Talk About Safety Signs and Signals
Safety signs are colored RED, YELLOW, GREEN, BLUE
Red–Prohibition signs
E.g. Ban certain action No entry etc.
Yellow– Warning signs
Have a black band on the edge of a triangle
E.g. Caution risk of electrical shock
Blue –Mandatory
Give instructions with a white symbol
E.g. wear hardhat
Green – Safe conditions
A square with a green background with white text
E.g. First Aid point
Toolbox Talks House keeping
Bad and untidy work place will lead to accidents mainly slips trips and falls.
Environmental problems can also occur with untidy work places.
i. Clean up as you go.
ii. Use the correct bin/skip for different types of waste materials.
iii. Do not obstruct gangways/walkways with tools and materials.
iv. Clean up all spillages immediately.
v. Position all cables and hoses in such a way that they do not produce trip hazards.
vi. Ensure that waste areas are protected from fires and fire hazards.
Toolbox talk Hazards of Reversing Vehicle
Reports show that 25% of plant and vehicles related accidents involve reversing vehicles.
Where ever possible:
i. Pedestrians should be separated from moving vehicles and plant.
ii. Keep a look out at all times for moving vehicles.
iii. All the vehicles should be fitted with both audible and visual warning systems.
iv. Never cross at the rear of a reversing vehicle as the driver may not see you.
v. Visiting vehicles should be given information about reversing hazards when entering on the project sites.
vi. Always wear high visibility clothing issued to you and if it requires replacement do it.
Toolbox talk – Cartridge Hammers or Rivet Guns
i. Only be used by trained persons issued with a certificate.
ii. Read makers instructions carefully before using gun.
iii. Before handling gun make sure it is not loaded.
iv. Load gun with barrel pointing in a safe position away from you.
v. Never place your hand over the end of the barrel.
vi. Never walk around with a loaded gun-load on site.
vii. Allow at least 75mm from edges of concrete or brickwork.
viii. Hold gun at Right angles to the job when firing.
ix. Wear goggles and ear defenders when using the gun.
x. In the event of a misfire, re-fire if nothing happens wait a further minute before unloading.
xi. Keep the gun clean and well oiled.
xii. Never leave the gun loaded when not in use.
Discover more from Method Statement Portal
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.